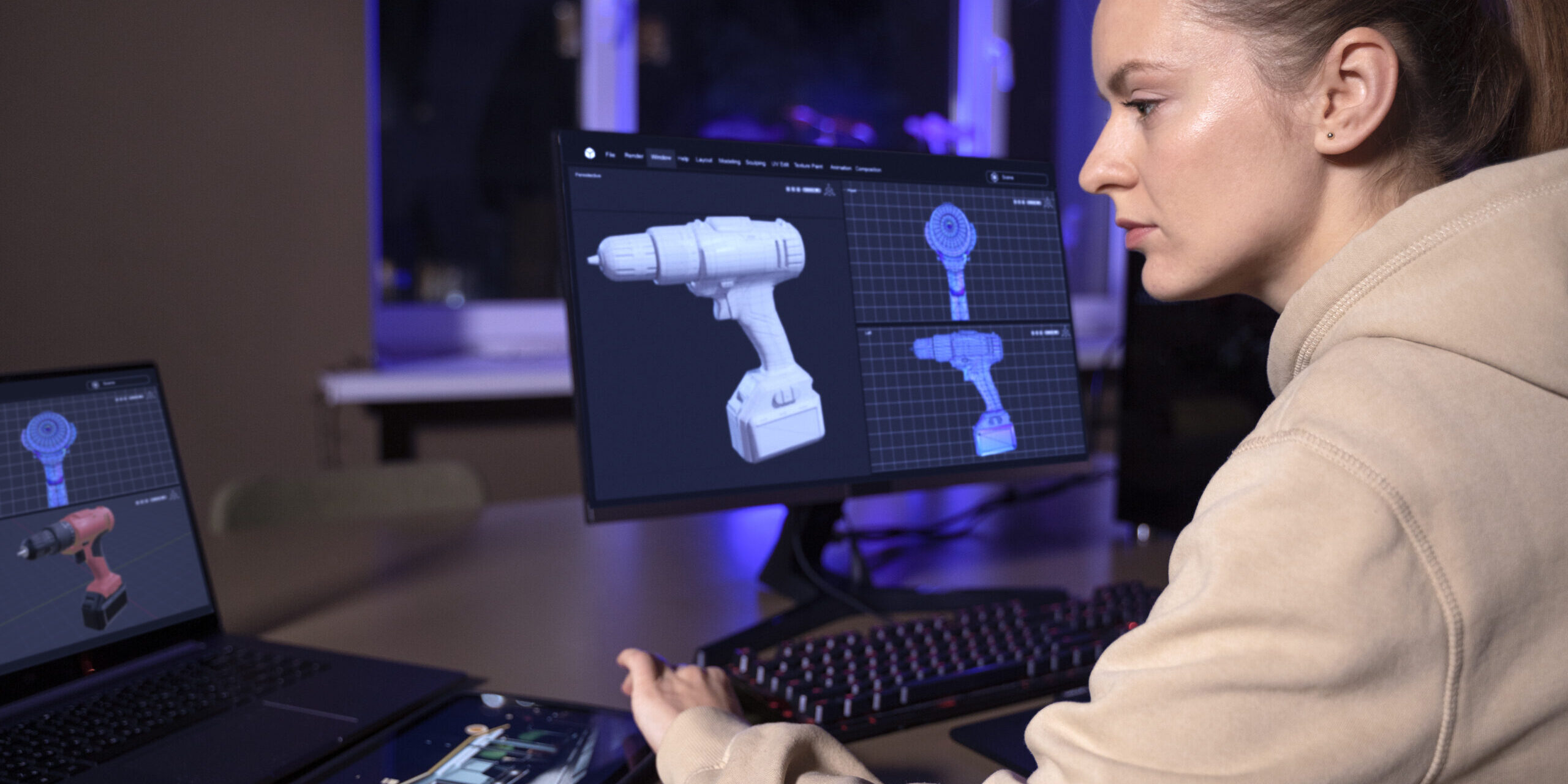
In today’s manufacturing landscape, ensuring the quality and dimensional accuracy of parts is paramount. Traditional inspection methods, while effective, can be time-consuming and limited in their ability to capture complex geometries. This is where 3D inspection using 3D laser scanning emerges as a revolutionary solution.
What is 3D Laser Scanning?
Imagine a technology that can create a digital replica of a physical object, capturing every nook and cranny with exceptional detail. That’s the essence of 3D laser scanning. A laser scanner emits a beam of light that strikes the object’s surface. The reflected light is then captured by a sensor, along with information about the beam’s travel time. By meticulously scanning the object from various angles, the scanner builds a vast collection of data points, forming a precise point cloud. This point cloud represents the object’s 3D geometry, allowing for comprehensive analysis and inspection.
Why Use 3D Laser Scanning for Inspection?
Traditional inspection methods often rely on physical gauges or coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). These techniques can be effective for simple geometries but become cumbersome and time-consuming for complex shapes. 3D laser scanning offers several advantages:
- Speed and Efficiency: 3D scanners can capture vast amounts of data in a single scan, significantly reducing inspection time compared to traditional methods.
- Accuracy and Precision: Modern 3D scanners boast high accuracy levels, capturing intricate details and minute deviations from design specifications.
- Non-Contact Inspection: Laser scanners operate without physically touching the object, eliminating the risk of damage to delicate parts.
- Versatility: 3D scanners can be used on a wide range of materials, from metals and plastics to even soft and reflective surfaces.
- Digital Documentation: The captured 3D data creates a permanent digital record of the inspected part, facilitating traceability and future reference.
How Does 3D Inspection Using 3D Laser Scanning Work?
The 3D inspection process using laser scanning typically involves these steps:
- Preparation: The object to be inspected is positioned and secured on a stable platform. Depending on the scanner and object complexity, reflective markers might be placed on the surface to aid in data alignment.
- Scanning: The 3D scanner is operated to capture data points across the entire surface of the object. This may involve moving the scanner around the object or, in some cases, rotating the object on a turntable.
- Data Processing: The collected point cloud data is then processed using specialized software. This software cleans the data, removes noise, and aligns multiple scans if necessary.
- Inspection and Analysis: The processed 3D model is compared to a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model, the digital blueprint of the part. Deviations from the intended design are highlighted, allowing for detailed analysis of dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and potential defects.
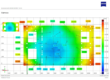
- Reporting: Inspection reports are generated, often featuring color-coded deviation maps that clearly visualize areas exceeding specified tolerances. These reports provide valuable insights for quality control and process improvement.
Beyond Inspection: The Applications of 3D Laser Scanning
3D inspection using 3D laser scanning finds applications in various industries beyond traditional manufacturing. Here are a few examples:
- Reverse Engineering: Existing physical parts can be scanned to create digital 3D models, enabling the recreation or modification of their designs.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: Historical artifacts and structures can be meticulously scanned for 3D documentation and preservation purposes.
- Medical Applications: 3D scanning can be used to create customized prosthetics and orthotics or for planning complex surgical procedures.
The Future of 3D Inspection
As 3D scanning technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in 3D inspection. Faster scan times, improved accuracy, and integration with artificial intelligence for automated defect detection are just a few exciting possibilities on the horizon. 3D inspection using 3D laser scanning is poised to revolutionize quality control across various industries, ensuring a future where precision and efficiency reign supreme.